Why another PDP11/70 project to run an emulated replica?
Just because the PDP11 series of computers built by DEC (Digital Equipment Cooperation) in the 1970s had a significant impact due to their role in the development of UNIX and the programming language C.
As a 16-bit minicomputer it laid the groundwork for todays CPU designs.
The PDP11/70 variant has been launched in 1975 running a 5 MHz CPU including an MMU able to address 8 MB of memory.
This project is simply combining the great work of the following developers:
- Jörg Hoppe who developed the SIMH Realcons extensions and the JAVA panels [3][4]
- Oscar Vermeulen who offers a real hardware replica of the PDP11/70 panel [5][6] and curated a number of operating systems [14][15][16][17]
- The SIMH team who developed emulators for important computer systems like the PDP [7][8]
Supported target platforms to run the emulation:
- Linux (e.g. Ubuntu 24)
- Raspberry PI (tested on a model 2 running a 32Bit Rasbian)
Download the source code from Github and Installation
$ git clone "https://github.com/shotto42/PDP11_Emulator.git"
$ cd pidp11/src # Go into the src directory
$ ./install_dependencies.sh # Install all required dependencies
$ ./install_pdp11_operating_systems.sh # Curated OSs by Oscar Vermeulen
$ ./make_simh.sh # Compile the SIMH and REALCONS
$ ./make_panel.sh # Compile the JAVA based PDP panelsRun the PDP11/70 Panel and the SIMH Emulator
$ cd pidp11 # Go into the main directory
$ ./start_panel.sh # The PDP11/70 panel needs to be started first
$ ./start_pdp11.sh 211bsd # Start the emulator (e.g. 211bsd as on OS)Raspberry PI configuration to establish a remote connection
$ sudo raspi-config
# Activate SSH to access without keyboard and HDMI monitor
Interface Options -> SSH
# Activate VNC when the Real VNC Viewer [22] is used to access the
Interface Options -> VNC Raspberry PI desktop
# Make sure that the whole SD card is used for the Rasbian OS
Advanced Options -> A1 Expand Filesystem
# Activate X11 to enable the app GUI forwarding via SSH (e.g. MobaXterm [21])
Advanced Options -> A6 Wayland -> W1 X11Examples
PDP11/70 emulator and cool-retro-term [23] running 2.11BSD UNIX on a LINUX Ubuntu system

Remote Raspberry PI access via MobaXterm [21] on Windows 11 using SSH and X11 forwarding
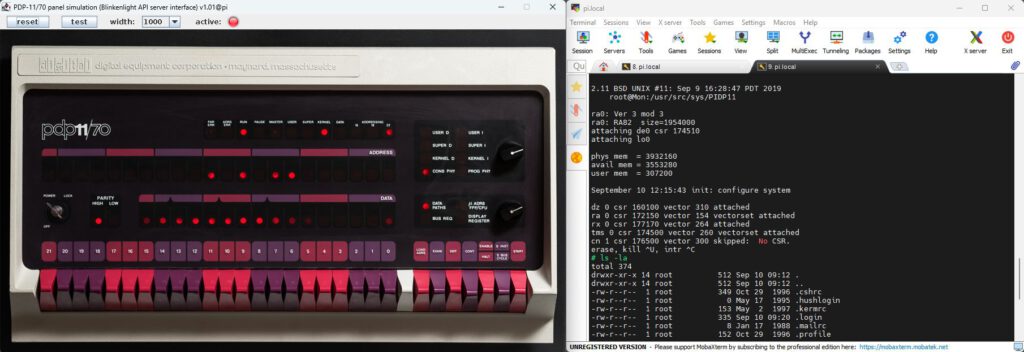
Operating Systems curated by Oscar Vermeulen
Standard [14]
| OS | Description |
| DOS-11 | First OS for the PDP11 by DEC |
| RT-11 | Small single-user real-time computing system by DEC |
| RSX-11MP | Multi-user real-time operating system by DEC |
| RSTS/E Version 7 | Multi-user, time-sharing operating system by DEC |
| 2.11BSD | UNIX by Berkeley Software Distribution |
| UNIX 5, 6 and 7 | UNIX variants by Bell Labs |
| System III and System V | UNIX variants by AT&T Unix Support Group USG |
Add-On [15][16][17]
- Paul Nankervis Collection of Operating Systems (needs to be loaded separately) [15]
- 2.11BSD Chase Covello’s updated version (installed via ./install_pdp11_operating_systems.sh) [16]
- RSX-11M-PLUS V4.6 (Johnny Billquist’s latest version with BQTC/IP (installed via ./install_pdp11_operating_systems.sh) [17]
Documentation, Tutorials and Software
- bitsaver.org archieved interesting PDP11/70 documents from manuals to detailed schematics [9][10]
- learningpdp11.com provides a lot of interesting blog posts to learn more about the operations of the PDP11 [12]
- dave.cheney.net has an interesting article covering the PDP11 inventions and architecture [13]
- PDP11 software is archieved by bitsaver.org [11]
- Another PDP11/70 emulator (web based) by Paul Nankervis can be found here [18]
SIMH Commands
For the full SIMH documentation go to [19]
PDP11 specific SIMH configuration documentation can be found here [20]
| OS | Description |
| CTRL-E | Enter the SIMH command line |
| CONTINUE | Continue the emulation of the machine |
| EXIT | Leave the emulator |
Fix in case of RPCBIND issues
$ sudo systemctl enable rpcbind
$ sudo systemctl start rpcbind
$ sudo setcap CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE=+eip /usr/sbin/rpcbindReferences
